Customer segmentation is a core aspect of ecommerce that drives sales, boosts customer loyalty, personalizes your marketing campaigns and promotes long-term business growth.
But, how do you go about it effectively?
Conducting an RFM analysis is key. It’s a simple but effective method of segmenting customers that helps you understand who your most valuable customers are.
Here, we’ll explore the strategy in detail and explain how it’s used for creating effective customer communications and predicting future customer behavior. Then, we’ll run you through how to get started with a step-by-step guide.
What is RFM Analysis? (Recency, Frequency, Monetary Value)
RFM analysis is a customer segmentation method that looks at the spending habits of existing customers. In particular, it tracks the following KPIs:
- Recency: When did a customer make their last purchase?
- Frequency: How often do they usually buy from you?
- Monetary value: How much do they spend?
Together, these factors — customer transactions, purchasing behavior, and customer spend — paint a picture of how engaged, loyal, and valuable a customer is.
These valuable insights will give you an objective basis for determining which customer group is the most profitable to pursue, and which is at the highest risk of churn.
With this window into customer behavior, you can adapt your marketing efforts and improve engagement with new customers and loyal ones alike.
How Does RFM Analysis Work?
To perform RFM analysis, you need to start by assigning an RFM score to each customer based on three key factors.
Start by creating profiles for your entire existing customer base — something that is typically achieved with the use of CRM (customer relationship management) software.
You then assign them RFM scores for each factor, typically on a scale from 1 to 5, based on how recently they made a purchase, how often they buy, and how much they spend.
Customers with a high frequency RFM score or a high monetary value are considered high-value and the most important to target. Whereas customers who score low in the recency corner may need extra attention to keep them engaged.
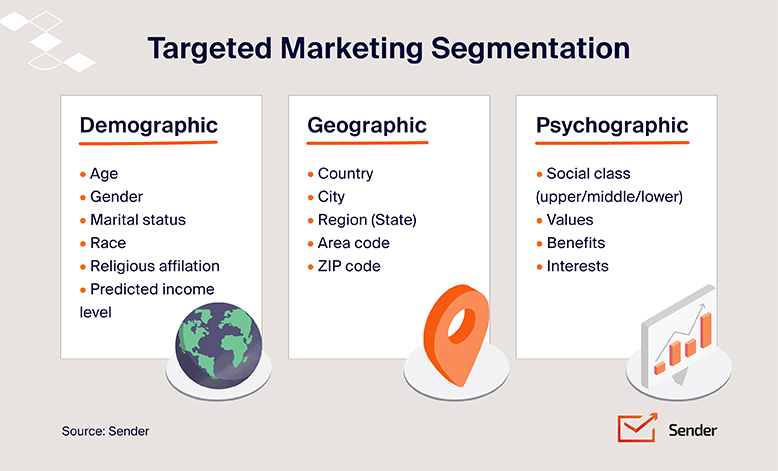
RFM analysis is useful because you can use it to complement your existing segmentation methods, such as grouping customers by geographic location or age, gender, interests, dislikes, etc.
This allows you to create highly targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to engage readers, prompt them to take an action, and ultimately, generate sales.
Want to see some real life examples? Check out these 17 marketing campaigns examples.
RFM Analysis Benefits
The RFM method offers manifold advantages for marketers, including:
- Opportunities for personalized marketing: RFM allows you to develop tailored marketing campaigns that resonate with the needs of each segment, boosting overall customer engagement. 76% of customers are more likely to buy a product from a company that personalizes;
- Reduced customer churn: It helps you spot at-risk customers early on, giving you a chance to re-engage them before they shop with a competitor brand. McKinsey found that 78% of customers are more likely to make repeat purchases from companies that use personalization to do this;
- Efficient budget use: RFM identifies your most valuable customer segments, meaning you can prioritize your marketing efforts for campaigns that will deliver the best return.
RFM Analysis for Customer Segmentation
RFM analysis plays a key role in segmentation because it builds clear customer personas with pre-defined qualities or characteristics.
RFM focuses on the psychology of their shopping habits. This means you can develop unique ‘styles’ for how you approach these customer segments, regardless of the specific products you’re trying to push.
Let’s say a customer scores low in the recency measurement and high in the monetary value measurement.
Using RFM analysis, you’d know a win-back style campaign would be effective to get them shopping with you again. And that it may be worth offering a better discount because they’re likely to become one of your most valuable customers if retained.
As you can see, RFM informs what kind of marketing style or strategy you should go for. It’s other personalization methods, such as tracking particular interests or browsing histories, which would inform the specifics of your product recommendations.
Steps of RFM Analysis
In this section, we’ll run through the steps involved to set up a successful system for RFM analysis and implementation of a targeted marketing strategy.
Building the RFM Model
To build an RFM model, you’ll analyze customer data and assign scores for recency, frequency, and monetary value on a scale (often 1-5). For the technical side, data can be extracted from your CRM or other customer database. You can use a machine learning model to automate this process or opt for CRM software with this built-in feature.
In any case, it’s essential to decide the specific boundaries that dictate when a customer advances to a new segment.
For instance, you could categorize “high-value” customers as those spending above a certain amount or “loyal” customers as those who make frequent repeat purchases.
Finally, make sure that your model automatically updates with new data over time, since customer behavior is likely to change as their relationship with your business shifts.
Segmenting the Customer Base
Once the RFM model is ready, the next step is to categorize customers. Here are some RFM segments you could create, plus some engagement strategies that are likely to be effective for each:
- Champions: High-value customers who frequently purchase — offer exclusive rewards or early access to new products to maintain their loyalty;
- Potential loyalists: Other customers who buy often but haven’t hit the highest frequency score yet — encourage their loyalty with personalized incentives like targeted discounts;
- Win-backs: Previously active customers who haven’t purchased recently — use win-back campaigns with appealing offers that reignite their interest;
- At-risk: High spenders whose purchasing frequency has declined — re-engage them through personalized messages or surveys to understand and address their needs;
- Repeat customers: Buyers with consistent, frequent purchases — provide loyalty programs or referral rewards to strengthen their relationship with your brand.
For your SMS and email campaigns, Sender’s generous free plan is particularly ideal here. It offers unlimited segmentation and has a multitude of integration options, so you can leverage your CRM and ecommerce data.
Selecting Target Customer Groups
Matching customers to a customer group isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach; there can be overlap. For instance, a customer could qualify for both “Champions” and “Loyal Customers” and receive multiple campaigns.
White looking at historical data, such as purchasing behavior and prior campaign responses, your RFM analysis should also take into account other customer data, such as their interests or browsing history.
If, say, your RFM analysis identifies a DIY enthusiast as a “Champion,” they could receive personalized offers for home improvement tools through campaigns emphasizing their loyalty and high spending.
Developing Personalized Marketing Strategies
If RFM analysis is the science of marketing, then personalized campaigns are where you can get creative.
After you segment customers, start developing your personalized marketing strategy with relevant messaging.
With tools like generative AI, you can craft customized emails filled with product recommendations that are likely to engage specific segments. But keep in mind, direct mail marketing might be more effective for some customers.
Remember, the goal is to connect with each segment on a personal level and drive repeat purchases. So, try out a variety of marketing strategies with different groups and see what works best for each, whether it’s a win-back style campaign or a loyalty reward system.
Analyzing Customer Response Patterns
Once your personalized marketing strategies are in play, it’s essential to analyze how customers respond.
Do your Champions engage most with loyalty perks? Are your Potential Loyalists taking up the offers that convert them to high-value status?
You should monitor key indicators like open rates, click-throughs, and purchase behavior for each customer group. When you identify trends and gauge which strategies are working, you can better predict future customer behavior and adjust your tactics to match.
Implementing Marketing Campaigns
When it comes to implementing a wider marketing campaign, the timing is absolutely essential.
You should use the valuable insights you gained from your RFM analysis to deliver the right messages at the right time to each customer segment.
Repeat customers might receive an email series reinforcing the value of your loyalty program, while win-back campaigns could focus on highlighting new products or limited-time discounts to revive interest.
With automation tools, you can ensure these campaigns roll out smoothly and reach valuable customers when they’re most receptive.
Although automation tools can help you increase scale and efficiency, ensure that you remove AI detection clues from your content before you hit publish.
Monitoring and Adjusting Strategies
Effective marketing is a continuous process, not something that you set and forget about.
You should monitor each campaign’s performance and make adjustments as needed based on the customer data you collect. For instance, if an at-risk customer segment isn’t responding well to your current approach, consider testing a different messaging style or timing.
The best way to test multiple marketing strategies is to use a method known as A/B testing. This involves creating two versions of the same campaign, each with a small variation — maybe one version uses a different email subject line and the other offers a different discount code.
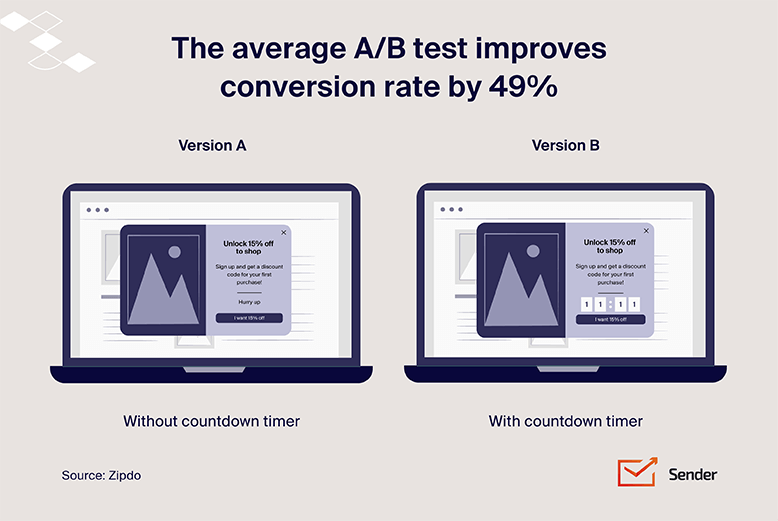
You then divide your audience into two groups and send one version to each, tracking which campaign gets better engagement.
Over time, you’ll spot which campaign elements tend to be the most effective, until you’ve got a formula that’s pretty effective at ‘leveling up’ customers in your RFM segmentation tier list.

