STP marketing is the cornerstone of modern digital advertising.
Many marketers, however, do it somewhat intuitively or by acquiring the skills through practice. Yet, to use STP full form in marketing and to take advantage of the approach completely, the theory needs to be understood.
In this article, we’ll go through what STP stands for, how it’s used in the real world by well-known brands, and the theoretical strategy of the approach. By the end of the article, you’ll know everything that you need in order to make STP marketing effective.
What is STP Marketing?
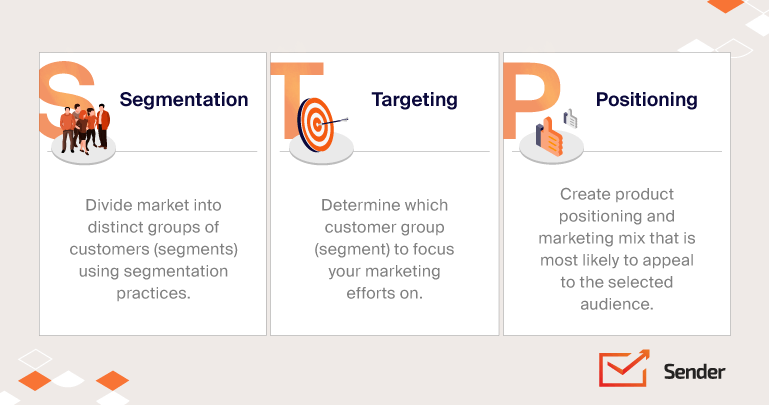
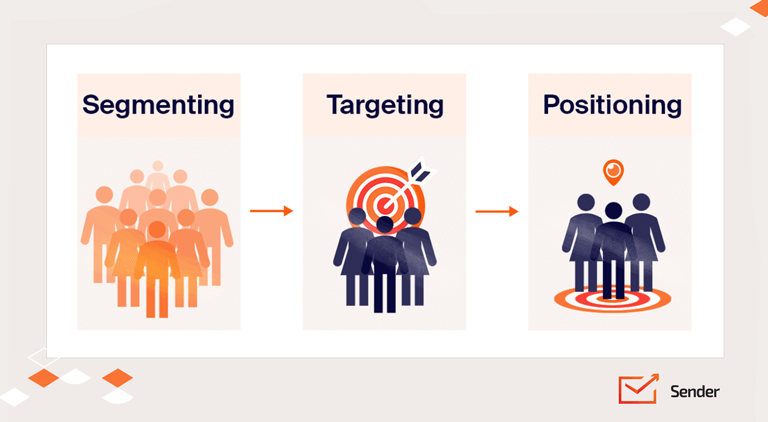
STP marketing is actually really easy to define and explain – STP stands for “segmentation, targeting, and positioning”. In simpler terms, the STP process combines three separate marketing approaches into one model. In practical application, STP marketing means creating market segmentation, targeting the selected segments, and adjusting product or service positions accordingly.
The importance of STP marketing cannot be overstated. It brings with it numerous advantages. For example, 91% of consumers are likelier to buy from brands that provide personalized and relevant offers. Additionally, 80% of frequent shoppers only buy from brands that personalize the experience.
In a nutshell, STP marketing is the way to make the above preferences of consumers work in your favor instead of against them.
Segmentation Targeting and Positioning Strategy
Segmentation
We have gone through segmentation in previous blog posts quite extensively. We will, however, give you a quick rundown on segmentation as it’s the first step in STP marketing.
Segmentation is the assignment of characteristics to your entire customer base and separating them into several different audiences based on data acquired. There are four types of customer segmentation that are used frequently:
- Geographic segmentation: Based on location, country, state, region, etc.
- Demographic segmentation: Based on age, gender, occupation, etc.
- Behavioral segmentation: Based on why, how, and how frequently users interact with your website, apps, or store.
- Psychographic segmentation: Based on factors such as lifestyle, habits, hobbies, activities, etc.
Of course, more than four segments can be created, but the ones outlined above are the most frequent ones. They are then used to decide what type of advertising and what kind of products or STP customer service would be most enticing to those segments.
One of the best ways to segment and target your audience is to use email marketing. It’s fast, easy and affordable.
Also read: Email List Building: 13 Email List Building Strategies
Targeting
When you have created four or more segments, it’s time to find the most valuable ones. Usually, if you’ve been in the business for some time, finding the most profitable ones will be intuitive.
You can, however, take a different approach and use data to support targeting. Certain data points can help you find the ideal segment:
- Size: Larger segments with more growth potential are always better.
- Profitability: It may be a little hard to calculate profitability, but taking customer lifetime value (CLV) into account and other data is a good way to predict segment profitability.
- Reachability: As a corollary to profitability, reachability is another important data point. Usually, customer acquisition cost (CAC) hedged against profitability metrics is a great way to conclude.
While there are more data points to consider, combining size, growth, profitability, and reachability will let you arrive at simple but powerful conclusions. Targeting can be made even more accurate, but resource cost rises in tandem. For many businesses, the three data points above will be enough.
Also read: What is Targeted Marketing? Definition, Strategies & Examples
Positioning
Once the other two steps are completed, a natural question arises – how to best position the product or service? The goal of positioning is to connect with the audience on a personal level and, possibly more importantly, set yourself apart from the competition.
Before getting onto the three important factors of positioning, it’s important to note the communication part. Every positioning is done through some content that should resonate with the audience. Using buyer persona or, at the least, analyzing the reasons and feedback provided by customers will let you craft more enticing communication.
When only positioning is taken into account, however, there are three important factors to be considered:
- Symbolic positioning: Also known as lifestyle positioning. You can figure out symbolic positioning by asking what kind of image is being projected. A great example of powerful symbolic positioning were the “Marlboro man” commercial used several decades ago.
- Functional positioning: What particular problems your products or services solve and how they make their lives easier.
- Experiential positioning: What experience and emotions your products and service provided to customers.
Again, there are more positioning factors that could be taken into account; however, in most cases, the work would be superfluous.
One of the best ways to support your understanding of positioning is to write out your own ideas about the “why, what, how” of your products and services. Then collect all the feedback provided by customers that match at least one of the factors. Such a segmentation targeting and positioning example grants you the ability to gain a more objective outlook on how your products and services are positioned.
STP Examples and Cases Studies
The STP approach has been used by many global brands to achieve success. While each company has used the STP framework differently, all have gained some measure of benefit from it. We’ve narrowed down STP marketing examples and case studies for several famous brands so that you can better take advantage of the strategy.
Apple Market STP
Apple Inc.’s segmentation, targeting, and positioning can seem quite counterintuitive when compared to how successful the company has been.
While they target a segment that appreciates design, quality, and performance, which creates a very wide audience, they also market themselves well-off individuals.
As you may well know, Apple products are considered premium and expensive. They primarily target those who can pay extra for small optimizations in performance or minor tweaks in design choices. Additionally, they reinforce the idea of paying extra by removing certain features such as headphone jacks from new products.
However, positioning their product as a premium, high-performance, and slick product, allows them to get the attention of those with the highest amount of buying power. Essentially, Apple focuses on lifestyle segmentation the most, since their products are the epitome of “paying for the brand name”.
Within the segment, Apple seems to focus on business professionals, audiophiles, designers, and teenagers. While the last one may seem odd, they are an audience that is extremely susceptible to “premium lifestyle” marketing, making targeting naturally effective.
STP Analysis of Nike
Nike is another giant that has successfully used STP marketing to its advantage. However, their approach has been slightly different from Apple’s.
They have approached an audience that consists of teens and young adults that have a focus on athletics. Additionally, they have a more extensive psychographic variable by attempting to capture high-achievers through inspiration and motivation.
As such, you’ll often see Nike appearing in nearly all sports, numerous ads with famous athletes, and supporting products (e.g. Nike’s training club or running app). However, they attempt to position their product as something available to all by making it seem that athletics can be done by anyone.
Amazon STP
Amazon uses the broadest available segmentation of target market. In fact, in many cases, there isn’t that much targeting and segmentation involved as they try to reach all demographics, geographics, and psychographics of consumers.
However, they do position themselves in a subtle manner. Their method is called anticipatory positioning as they attempt to introduce products right as demand begins to appear. A great example of such positioning has been Amazon Web Services. As said in their 2018 annual report:
“We must invent on their behalf. We have to tap into our own inner imagination about what’s possible. AWS itself – as a whole – is an example. No one asked for AWS. No one. Turns out the world was in fact ready and hungry for an offering like AWS but didn’t know it.”
Thus, a significant part of their positioning strategy is anticipating demand before everyone else. In other cases, Amazon might start developing its own products that beat the competition (Kindle is one example).
Coca-Cola Segmentation Targeting Positioning Analysis
Coca-Cola is another company that has a sort of ubiquitous product. Of course, it can hardly be the case otherwise, as it’s the largest beverage company in the world. Again, its targeting and segmentation is so wide there’s barely anything to speak of.
Their product positioning, however, is something to talk about. Primarily, they try to position their drinks as something that brings happiness and well-being. As such, you should have noticed a wide array of advertisements involving families, friendships, and holidays.
In fact, Coca-Cola has such a strong connection to Christmas that its designers are often credited for solidifying the color of Santa Claus’ suit (original incarnations of the symbol used tan). Even if this story isn’t true, Coca-Cola has positioned its products so well that they have become intertwined with Christmas – a celebration of family and happiness.
McDonald’s STP Model
McDonalds primarily targets low to middle-income segments. It’s definitely not a premium brand, but it is accessible. As such, it can target a wide variety of low to middle-income people.
Additionally, the products are nearly always adjusted for specific geographic locations. Menus in India are very different from the ones in France. These differences are not due to logistics. Mcdonald’s investigates cultural preferences in each country before developing a menu in order to match the target audience better.
Similarly to Coca-Cola, Mcdonald’s position itself as something that brings joy to families. In fact, Ronald McDonald, the mascot, replaced their previous symbol because the clown figure was a lot more popular with children.
Start Refining STP Marketing Model Now
STP marketing has led many companies to run significantly more effective campaigns. There’s no good reason why any business, especially a digital one, would avoid using STP. With all the data available nowadays, the process is much easier than before, but nets the same great benefits.
Want to use email and SMS marketing for your STP campaigns? Look no further! Sender will provide you with all the tools you need to run the most effective marketing campaign yet!
Start with zero financial commitment, the FREE Forever plan can help you do just that. Send up to 15,000 emails a month to up to 2,500 contacts absolutely free of cost!
All features, including multichannel automation ( Email + SMS), are also included for free users.
Also read:

